Development of Side-Effect-Free Diabetes Cure
Applying the new delivery system “Biozipcode” to develop drugs that act directly on “Diabetes Stem Cells,” which are considered the cause of diabetes.
For the discovery and research on Diabetes Stem Cells, please refer to this page.
Difference Between Molecular Targeting and Cell Targeting
Technology to Deliver Drugs Only to Necessary Parts
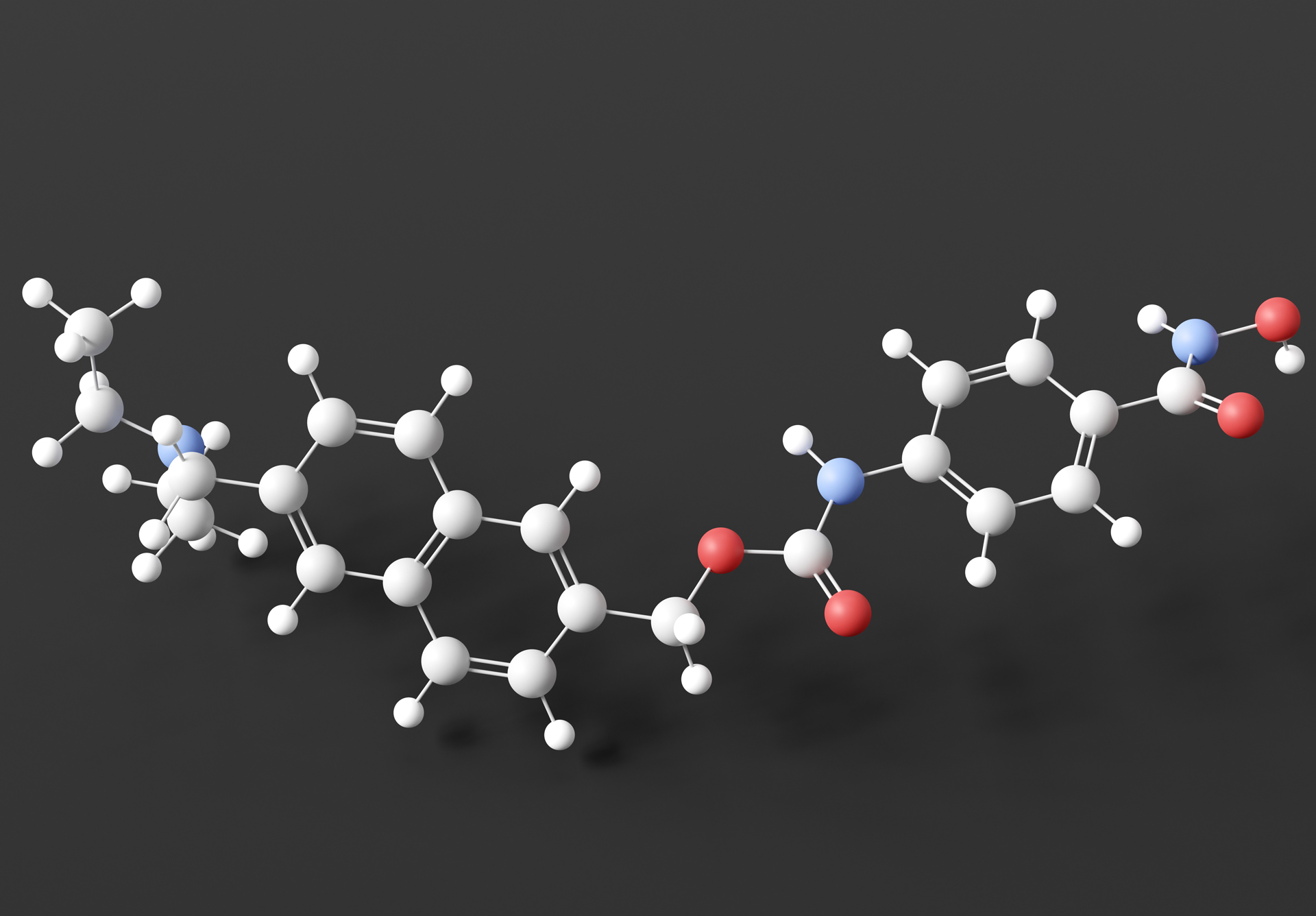
It has been found that the combination of insulin and HDAC inhibitors may be effective in achieving remission of diabetes and its complications. However, HDAC inhibitors (such as givinostat) are known to have some side effects and have been harmful to some mice when administered alone, so further research on the safety of the treatment is needed.
Therefore, by applying the Biozipcode technology, it is possible to deliver drugs to act selectively on organs and cells, rather than at the molecular level.
Discovery and Research of Diabetes Stem Cells
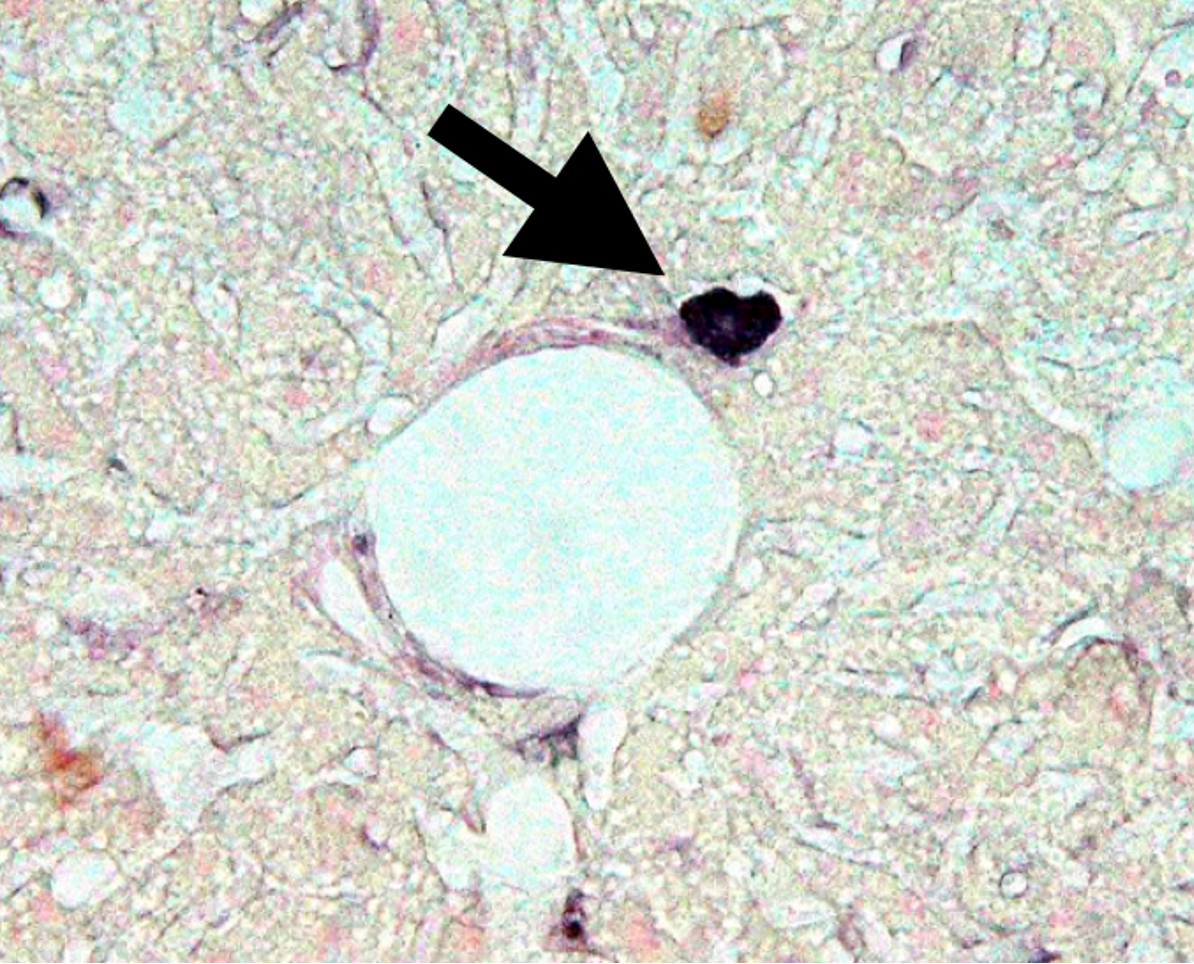
Abnormal cells were found in hematopoietic stem cell fractions that cause diabetes, which do not disappear even when b/s levels are normalized, creating refractory characteristics.
Discovered that diabetes is a disease caused by abnormalities in hematopoietic stem cells and developed a method to cure diabetes by isolating and eliminating “Diabetes Stem Cells.”
Cell Targeting Technology (Biozipcode)
Aiming to develop cell-targeted drugs as a new drug delivery method for the next generation, beyond the current era of molecular-targeted drugs.
Developing a completely new diabetes and diabetes complication cure using Biozipcode that causes no side effects.
Using cell targeting technology with Biozipcode to develop side-effect-free anticancer drugs, providing treatments that minimize patient burden.
Aiming to develop scaffold materials that promote natural wound healing, adhering to tissues without the need for transplantation or suturing, and enhancing quality of life (QOL).
Are You Interested in Research at the Department of Regenerative Medicine?
Are You Interested in Research at the Department of Regenerative Medicine?
You can send a direct inquiry to the Department of Regenerative Medicine through the contact form.